The 7 Most Powerful Natural Hacks to Heal Your Gut
Your gut is the foundation for all other facets of your health. It affects every aspect of your life, including your mood, weight, cognitive function, and even hormonal issues like menopause. So how do you ensure that yours is in good shape? Are there natural ways to heal your gut when it gets compromised?
Home to trillions of bacteria (that could be bad, good, or neutral), the gut is collectively known as the “gut microbiota.” Everything you eat goes through this little ecosystem before it gets chucked out via your digestive system.
The Importance of Gut Health
Your gut performs a multitude of functions, including:
- Digestion of food by enzymes in your digestive tract
- Absorption of nutrients from foods you’ve eaten
- Acidification of stomach contents to aid digestion
- Metabolism of fats and carbohydrates into energy (glycogen) for your body cells
- Regulation of your blood sugar levels by hormones released by your intestinal cells
When your gut microbiome turns out of whack, other essential body functions, such as immunity and brain function, are also hampered. Long-term effects could include the development of chronic illnesses like metabolic disorders, autoimmune diseases, and mental health problems, among many others.
Boosting your gut health is the crucial first line of defense when something seems off – whether you’re having digestive symptoms like bloating or other seemingly unrelated symptoms like joint pains.
You’ve got to have a strong gut to have a healthy body and mind! The good news is that you can naturally heal your gut. Simple dietary and lifestyle adjustments will have a profound impact not only on your gut health but on your overall health and well-being.
What messes up your gut health?
Many dietary, lifestyle and environmental factors brought on by contemporary living can negatively affect your gut health. These include:
1. Gut-damaging foods and drinks
- Gluten – includes barley, wheat, rye, and others. Gluten can lead to stomach pain, bloating, and fatigue, especially for celiac disease patients.
- Dairy – milk, soft cheeses, and other unfermented dairy products. Some diet plans allow dairy products like butter and yogurt, but others don’t. This largely depends on your food sensitivities or food allergies.
- Sugar – maple syrup, white processed sugar, and any sugar in all forms, including high-sugar fruits, fruit juices, and fizzy drinks. Added sugars can lower the diversity and number of good bacteria in your stomach and cause inflammation. Even worse, a gut imbalance can trigger sugar cravings, increasing consumption.
- Grains – all grains, including corn and pseudo-grains like quinoa, buckwheat, and amaranth. They do not entirely digest in your body; thus, they pass through the lining of your gut intact.
- Nightshades – eggplant, potatoes, pimentos, tomatoes, tomatillos, goji berries, and peppers. If you are sensitive to nightshades, you may have problems with bloating, diarrhea, heartburn, and joint discomfort due to inflammation because you can’t digest them effectively.
- Nuts and seeds – almond, walnut, pistachio, and others. They contain unsaturated fatty acids and fiber, which may harm your beneficial gut bacteria. Gut healing diets usually eliminate all nuts and seeds at first but can be added back later.
- Beans and legumes – lentils, soybeans, peanuts, and others. They are high in carbs and starches, which are difficult to digest. They are also high in lectins that interfere with the absorption of minerals and are linked to obesity and chronic inflammation.
- Raw veggies – broccoli, brussels sprouts, cabbage, and other cruciferous vegetables. It’s best to skip eating them while healing your gut since they are also extremely difficult to digest due to their high insoluble fiber content.
- Processed foods – bacon, sausages, fast foods, and many others. They lack the beneficial bacteria and yeast that regulate your gut flora and help prevent chronic conditions like irritable bowel syndrome.
- Processed, refined oils – corn, canola, soy, and others. They contain harmful additives and omega-6 fatty acids, which promote the development of gastrointestinal illnesses.
- Caffeine – coffee, chocolate, and energy drinks. Caffeine meddles with your adrenal glands and cortisol levels which can negatively impact your gut health.
- Alcohol – beer and hard liquor. Alcohol feeds bad bacteria and depletes the beneficial ones, promoting gut damage.
2. Stress
Stress may cause a spike in cortisol, leading to a leaky gut (compromised gut lining) and other digestive issues. It can make it harder for your body to absorb nutrients from food. It can also increase muscle tension in the intestines, resulting in constipation and diarrhea.
3. Disrupted Circadian Rhythm
Circadian rhythms regulate several processes in the gastrointestinal tract, including the transport of nutrients. Disruptions caused by irregular sleep/wake cycles and exposure to blue light at night can lead to an imbalance in your gut flora. Gut dysbiosis can cause circadian asynchrony and vice versa. Obesity, diabetes, and cirrhosis are just a few metabolic illnesses that can arise due to these abnormalities.
4. Medications
A wide range of prescription and over-the-counter drugs can adversely affect your gut health. They kill off the good bacteria in your gut, altering your gut flora. These include:
- Antibiotics
- Steroids
- Birth control pills
- NSAIDs (ibuprofen, aspirin, naproxen, and others)
- Acid-reducing meds for heartburn
Top Signs and Symptoms of an Unhealthy Gut
Several common symptoms could hint that your gut is trying to get your attention. As you might guess, digestive symptoms are the primary signs of an unhealthy gut. These may include:
- Bloating
- Constipation
- Diarrhea
- Indigestion
- Acid reflux or heartburn
- Stomach cramps
- Excessive gas
- Food allergies or food intolerances
- Unintentional weight gain or loss
However, since the gut microbiome is tightly related to other bodily systems, various non-gastrointestinal signs of a problematic gut may appear over time, such as:
- Skin issues
- Moodiness
- Brain fog
- Migraines
- Fatigue
- Anxiety
- Depression
- Insomnia
- Sugar cravings
- Dry or thinning hair
- Autoimmune conditions
- Female hormone imbalances
- Male hormone imbalances
7 Natural Hacks to Heal Your Gut
You have the power to heal your gut! To do so, you can talk with a functional medicine doctor who will carefully consider every aspect of your health and devise a plan tailored to your needs. This plan involves some diet and lifestyle hacks which may include the following:
1. Consume gut-friendly foods.
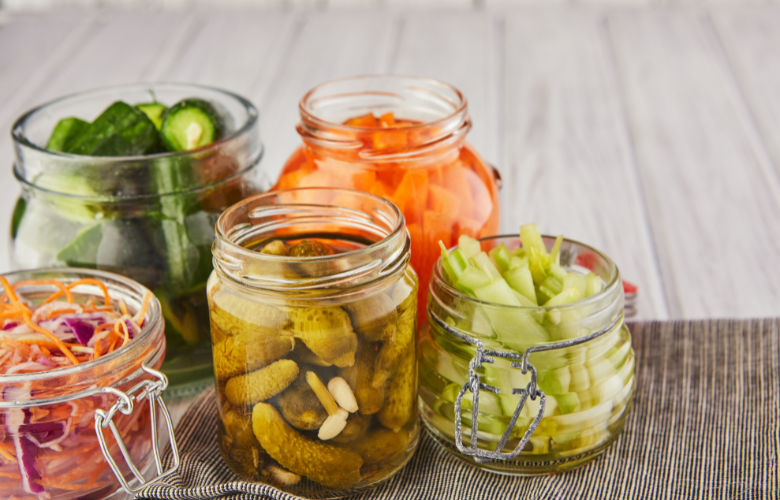
- Probiotics: include fermented foods like kefir, kimchi, miso, natto, sauerkraut, kombucha, and cultured yogurt. They increase good bacteria in your digestive tract and promote a healthy immune system.
- Prebiotics: asparagus, raw garlic, onion, artichoke, leafy greens, and fresh fruits like kiwi and pineapple. They feed the good bacteria to encourage their growth and diversity.
- Anti-Bacterials: clove, cinnamon, garlic, and oregano oil. They destroy harmful gut bacteria, relieve pain, reduce inflammation, and enhance cognitive function.
- Collagen-rich: eggs, fish with skin on, lean meat, and spirulina. Collagen facilitates digestion and nutrient absorption. It also has amino acids, which soothe, strengthen, and heal your gut lining.
- Broths and soups: chicken soup or bone broth. They are gentle for your digestive system. They are also a fantastic source of protein and amino acids, which are beneficial for digestion, nutrition, and immunity.
- Fatty fish: herrings, albacore tuna, salmon, and sardines. Your digestive health benefits greatly from eating fish high in omega-3 fatty acids. They can help fight inflammation and maintain the balance of bacteria in your gut. Additionally, they can strengthen the immune system and heal intestinal wall damage.
2. Repair your gut lining with soothing herbs.
It’s essential to consult a qualified herbalist or functional medicine practitioner before taking any herbs for the proper dosage. These can include:
- Aloe vera
- Basil
- Coriander
- Mint
- Parsley
- Rosemary
- Slippery elm
- Marshmallow root
- Turmeric
- Thyme
3. Stay hydrated.
Drinking enough fluids helps your body remove toxins, promote peristalsis, and keep your gut balanced. Dehydration impairs the function of your cells and makes it more difficult to pass stools. This could lead to the buildup of toxins in the digestive tract.
You can increase your fluid intake when losing more fluid due to exercise, sweating, or an ailment. You can also take herbal teas, which provide additional health benefits.
4. Manage your stress.
Being entirely stress-free is impossible. However, there are certain ways to reduce stress and lessen its negative effects on your health. Some of them are:
- Meditating
- Walking
- Diffusing essential oils
- Bonding with family or friends
- Spending time with a pet
5. Get enough sleep.
Get at least 7 hours of uninterrupted sleep each night. Keep good bedtime habits, such as sleeping on a regular schedule. Additionally, wear blue-light-blocking eyewear at night to reduce your exposure to blue light. It’s also best to avoid using screens for at least an hour before bed. Most importantly, always sleep in a cool, dark, quiet room.
6. Move, move, move!
Regular exercise is excellent for your digestive system. Aerobic exercise lowers your risk of developing colon cancer and can aid with bloating symptoms and bowel regularity. Remember, physical inactivity is one of the main risk factors for constipation. So move your body to help move your bowels!
7. Take gut-healing supplements.
Finally, on the advice of a trained professional, consider taking certain supplements to heal your gut. These may consist of the following:
-
- Digestive enzymes: aid in the breakdown of macronutrients. They can also alleviate post-meal discomforts, such as flatulence, bloating, and diarrhea.
- L-glutamine: an amino acid that fortifies and shields the intestinal lining.
- Fish oil: promotes the growth of good bacteria and lowers intestinal inflammation.
- Deglycyrrhizinated licorice root (DGL): is most frequently used to treat stomach ulcers because it helps intestinal cells grow and survive and restores damaged mucus membranes.
- Hydrochloric acid (HCL): Taking HCL before meals can improve how quickly your body digests and absorbs nutrients.
Final Thoughts on Healing Your Gut
Making small changes to your diet and way of life can improve your gut health. You don’t have to do this alone, so don’t feel overwhelmed! Consult a functional medicine doctor to help you on the road to gut healing. So that your entire body may heal, heal your gut!